
Mexico: A Key Globalization Partner in Trade and Exports
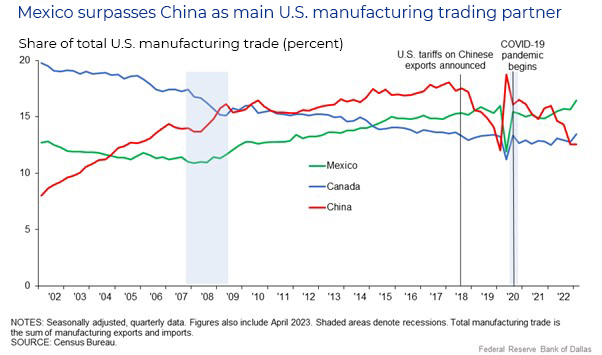
Mexico has emerged as a crucial globalization partner in the realm of trade and exports, showcasing its significant role in the global economic landscape. As the United States' primary trading partner, Mexico's relationships with neighboring countries and beyond illustrate how deeply intertwined trade dynamics can drive mutual growth and development. In this article, we will dive into the essential facets of Mexico's trade landscape, examining its partnerships, challenges, and opportunities.
The ongoing process of globalization continues to shape the economic interactions between nations, with Mexico at the forefront of this transformation. With its strategic geographic location, diverse economy, and an array of international trade agreements, Mexico stands to benefit significantly from enhanced globalization efforts. Understanding Mexico's role as a key player in global trade not only highlights its economic potential but also emphasizes the importance of collaborative growth in the modern world.
Overview of Mexico's Trade Landscape
Mexico's trade landscape is characterized by a combination of extensive exports and imports, resulting in a vibrant economic environment. As a significant globalization partner, Mexico engages actively with various countries, relying heavily on both regional and international trade agreements to facilitate its economic activities.
One of the cornerstones of Mexico's trade policy is its participation in the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which has significantly boosted cross-border trade with the United States and Canada. Following the transition from NAFTA to the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), these dynamics have continued to evolve, further enhancing Mexico's role as an essential trade partner.
The U.S.-Mexico Trade Relationship
The economic relationship between the United States and Mexico is one of the most robust in the world. The U.S. is Mexico's largest trading partner, accounting for approximately 80% of Mexico's exports. This close economic relationship has been largely facilitated by agreements such as NAFTA and the USMCA, which aim to reduce trade barriers and promote commerce.
Many industries in Mexico, including manufacturing, automotive, and electronics, have flourished due to the opportunities provided by this partnership. However, the dependency on the U.S. economy remains a double-edged sword, as Mexico's economy is vulnerable to shifts in U.S. policies or economic fluctuations.
The Impact of NAFTA and USMCA on Trade Dynamics
NAFTA, which was enacted in 1994, has had a profound impact on functional trade relationships between the U.S., Canada, and Mexico. This agreement aimed to eliminate tariffs on goods traded among the three countries, providing an unprecedented boost to economic growth, particularly in Mexico.
However, as trade dynamics continued to shift, various stakeholders raised concerns regarding the agreement's efficacy in addressing critical issues, such as agricultural subsidies and labor protections. In response, the USMCA was introduced in 2018 to enhance existing provisions while addressing some of the criticisms leveled against NAFTA.
The transition to USMCA has led to a more balanced framework for trade, while Mexico's emphasis on securing favorable terms with its partners has strengthened its status as a globalization partner. Nevertheless, the real challenge lies in the operationalization and enforcement of these agreements to ensure fair and equitable trade practices.
Key Exports and Imports: What Mexico Offers and Needs
Mexico's economy is diverse, with major imports and exports contributing to its overall economic activity. The country mainly exports manufactured goods, including machinery, steel, electronics, and automotive components, while its imports are often driven by consumer goods and machinery that support its growing industries.
Mexico's key exports can be outlined as follows:
- Machinery: Consistently ranks among the top exports, meeting the demands of both domestic and international markets.
- Petróleo: With the substantial output of crude oil, petroleum remains a crucial export product, especially to the U.S.
- Automotive Parts: Significant investment by foreign car manufacturers in Mexico has stoked growth in this sector.
Conversely, Mexico's imports predominantly consist of:
- Machinery: Integral to support manufacturing and technological growth.
- Consumer Goods: Encompassing electronics, clothing, and other products necessary for daily living.
The Role of the Service Sector in Mexico's Economy
The service sector plays a dominant role in Mexico's economy, increasingly contributing to GDP and employment. Particularly, tourism has risen to become the largest service industry, attracting millions of visitors each year to its various destinations, from historical cities to paradisiacal beaches.
As the tourism landscape matures, there has been a noticeable shift from traditional attractions to modern resorts, such as Cancún, which cater to international tourists. The service industry's growth goes beyond tourism, offering opportunities in finance, telecommunications, and other sectors that are crucial to support Mexico's integration into the global economy.
Challenges Faced by Mexican Farmers and the Impact of Subsidies
Despite the opportunities provided by globalization, Mexico's agricultural sector faces persistent challenges. Smallholder farmers struggle to compete against the influx of subsidized products from the U.S., which can dramatically affect their profitability and sustainability.
These agricultural subsidies often favor large-scale farming operations, thus creating an uneven playing field for Mexico's rural farmers. The impact of such policies raises concerns over the long-term viability of farming in Mexico, particularly in regions heavily reliant on traditional farming practices.
Gender Dynamics in the Labor Market
Another vital aspect of Mexico's economy is the participation of women in the labor market. The growing service sector has provided women with enhanced job opportunities, often leading to improved income levels in households. However, significant wage disparities persist, highlighting the need for policies that promote gender equity in the workforce.
Efforts to bridge this gap are crucial as women represent a significant proportion of the workforce, and their economic empowerment contributes to overall economic growth. Ensuring fair wages and equal opportunities will not only foster equity but also strengthen Mexico's appeal as a resilient globalization partner.
Government Revenue Sources and the Role of Pemex
Government revenue in Mexico stems from various sources, including income tax, value-added tax (VAT), and other levies. Additionally, the contribution from the state-owned oil company, Pemex, plays a pivotal role in funding public services and infrastructure through significant oil exports.
Oil revenues have been instrumental in supporting Mexico's economic development, yet the volatility of global oil prices poses risks. As the country seeks to diversify its revenue sources, improving the tax collection system and enhancing efficiency in public spending will be crucial to ensure sustainable growth.
Conclusion: Mexico as a Strategic Partner in Global Trade
In conclusion, Mexico's status as a globalization partner in trade and exports is evident through its strong economic ties, particularly with the United States. With a diverse economy and a strategic geographical location, Mexico has positioned itself as a pivotal player in addressing global trade issues and opportunities.
As challenges persist within agriculture, gender dynamics, and the need for revenue diversification, Mexico's continued growth will rely on its ability to adapt to changing economic conditions while fostering collaborative relationships with its trading partners. A steadfast commitment to addressing these concerns will ensure that Mexico remains a critical voice in the global trading system and a vital partner in the journey of globalization.
Did you find this article helpful? Mexico: A Key Globalization Partner in Trade and Exports See more here General.
Leave a Reply




Related posts