
Acetylcholine in Depression: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Depression is a complex mental health disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Recent research has highlighted the potential role of acetylcholine in depression, a neurotransmitter known primarily for its involvement in memory and learning. Understanding the intricate relationship between acetylcholine and depression is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies, as this neurotransmitter might influence various mood-regulating pathways in the brain.
This article aims to explore the multifaceted role of acetylcholine in depression, examining its functions, how it connects to depressive symptoms, and the causes linked to altered acetylcholine levels. Furthermore, we will discuss current treatment options targeting this neurotransmitter and consider future research directions that could provide new insights into depression management.
Overview of Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine is a vital neurotransmitter that plays a significant role in the central and peripheral nervous systems. First discovered in the early 20th century, acetylcholine facilitates communication between neurons and is crucial for muscle activation, memory formation, and various cognitive functions. In the brain, it is predominantly found in regions responsible for attention, learning, and memory, underscoring its importance in cognitive processes.
Acetylcholine is synthesized from acetyl-CoA and choline, and it functions by binding to specific receptors on the post-synaptic membrane, leading to excitatory or inhibitory cellular responses. Dysregulation of acetylcholine signaling has been associated with several neurological conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and depression, highlighting its significance in maintaining mental health.
The Role of Acetylcholine in the Brain
The brain's intricate signaling pathways involve neurotransmitters like acetylcholine, which operate through specific receptors known as cholinergic receptors. These receptors are classified into two main types: muscarinic and nicotinic receptors, each playing different roles in neurotransmission and affecting various brain functions.
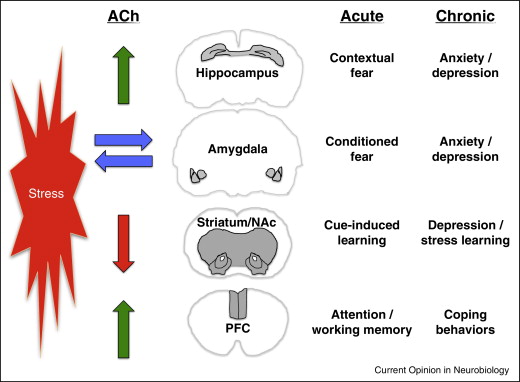
Research indicates that acetylcholine is involved in modulating attention, arousal, and memory consolidation. Furthermore, cholinergic neurons, which produce acetylcholine, can influence mood regulation, making them an essential area of study concerning mood disorders like depression. The balance of acetylcholine levels is fundamental to emotional stability; an impairment can contribute to the onset of depressive symptoms, demonstrating the neurotransmitter's profound impact on mental health.
Link Between Acetylcholine and Depression
The link between acetylcholine and depression has garnered increasing attention in neuropsychological research. Studies suggest that abnormal acetylcholine signaling may play a role in developing depressive disorders. For instance, low levels of acetylcholine have been observed in patients with major depressive disorder, potentially contributing to the cognitive deficits often experienced in conjunction with depression.
Additionally, acetylcholine's interactions with other neurotransmitter systems, such as serotonin and norepinephrine, could be significant in understanding its role in mood regulation. The interplay between these systems may help to elucidate why certain individuals are more susceptible to depression when acetylcholine levels fall out of balance.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalance: An imbalance in neurotransmitters, particularly a deficiency in acetylcholine, can lead to depressive symptoms.
- Genetic Factors: Some genetic predispositions may affect acetylcholine synthesis or receptor function, increasing the risk of depression.
- Chronic Stress: Prolonged exposure to stress can lead to alterations in cholinergic functioning, thereby impacting mood regulation.
- Age-Related Changes: Aging can lead to a natural decline in acetylcholine levels, which may contribute to the increased prevalence of depression in older adults.
Symptoms of Depression Affected by Acetylcholine
The symptoms of depression may present differently from person to person, but some common features can be linked to the dysregulation of acetylcholine levels. These symptoms include:
- Cognitive Dysfunction: Difficulties in concentration, memory lapses, and indecisiveness.
- Anhedonia: A marked inability to experience pleasure in activities once found enjoyable.
- Fatigue: Persistent feelings of tiredness or low energy, often exacerbating depressive symptoms.
- Sleep Disturbances: Changes in sleep patterns, including insomnia or excessive sleeping.
Recognition of the connection between these symptoms and altered acetylcholine levels can aid in formulating a targeted approach to treatment, potentially focusing on restoring normal cholinergic function as a means of alleviating depressive symptoms.
Current Treatment Options Targeting Acetylcholine
Current treatments for depression often include a range of psychotropic medications, including antidepressants. While traditional antidepressants predominantly target serotonin and norepinephrine systems, emerging evidence suggests that medications affecting acetylcholine levels may also play a role in alleviating depressive symptoms.
Cholinesterase inhibitors, commonly used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, increase the amount of acetylcholine available in the synaptic cleft by preventing its breakdown. Some studies indicate that these medications may also have a positive impact on mood regulation, representing a potential avenue for treatment in individuals experiencing depression, particularly those with cognitive impairments.
Moreover, the exploration of nicotinic receptor agonists as a potential treatment option for depression highlights the need for further investigation into how acetylcholine modulation could lead to improved mood outcomes. The integration of acetylcholine-targeting strategies alongside traditional antidepressant therapies may offer a more comprehensive approach to managing depression.
Future Directions in Research
The field of depression research is rapidly evolving, and the role of acetylcholine remains a critical focus area. Future studies are essential to deepen our understanding of the mechanisms through which acetylcholine in depression operates and to investigate the potential therapeutic applications that target this neurotransmitter system.
Research could benefit from exploring how acetylcholine interacts with various mediators of depression, including genetic factors and environmental influences. Additionally, investigating the efficacy of novel pharmacological agents that modulate cholinergic function could lead to more effective treatments for depression, particularly in populations with cognitive impairment.
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between acetylcholine and depression highlights the importance of this neurotransmitter in maintaining mental health. Understanding how acetylcholine affects mood regulation and contributes to depressive symptoms opens up new avenues for treatment. As we continue to explore the roles of various neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine, in depression, we may pave the way for innovative treatment strategies that offer hope to those affected by this debilitating disorder.
Incorporating interventions that target acetylcholine levels presents an exciting frontier in the fight against depression, emphasizing the need for ongoing research and clinical exploration to enhance treatment outcomes for individuals suffering from depressive disorders.
Did you find this article helpful? Acetylcholine in Depression: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment See more here Education.
Leave a Reply






Related posts