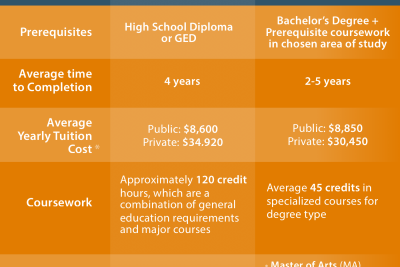
What benefits do coalitions offer in international relations

In the complex landscape of international relations, the formation of coalitions emerges as a pivotal strategy for states and non-state actors aiming to address shared challenges and objectives. These coalitions represent temporary alliances that mobilize resources and coordinate actions to achieve common goals, often in response to pressing global issues. As the dynamics of power shift and evolve, the role of coalitions becomes increasingly relevant, highlighting their potential to shape diplomatic outcomes and affect international policy.
Understanding the benefits that coalitions offer in international relations is essential for comprehending how nations collaborate and exert influence on the global stage. The effectiveness of a coalition can be appreciably linked to its ability to unify diverse interests and leverage collective strengths, thereby enhancing its capacity to pursue specific agendas. This exploration delves into the various advantages that coalitions provide, revealing their importance in modern governance and international politics.
What are Coalitions in International Relations?
In the context of international relations, a coalition can be described as a temporary alliance where distinct actors come together to work towards a common goal. These actors can range from sovereign states to intergovernmental organizations and non-state entities that unite for various purposes, such as addressing security threats, responding to humanitarian crises, or coordinating economic policies. The uniqueness of coalitions lies in their ability to adapt quickly to changing circumstances, allowing participants to engage in collective action without forming a permanent alliance.
Unlike more formal structures such as treaties or permanent alliances, coalitions are often characterized by their discrete objectives and flexible frameworks. The motivations for joining a coalition can vary, including pragmatic considerations such as shared security interests, economic benefits, or cultural ties. Importantly, while participants in a coalition may pursue a common goal, they often retain distinct national identities and priorities, which can influence their interactions and strategies.
Key Characteristics of Coalitions
Understanding the core characteristics of coalitions is essential to appreciate their role in international relations. One key trait is their temporary nature; members typically come together for a specific purpose and may disband once that goal is achieved or deemed unattainable. This characteristic underscores the dynamic and fluid nature of coalitions, differentiating them from more stable alliances.
Another important feature is the variation in interests among members; coalitions can comprise actors with divergent agendas that converge on a particular objective. For instance, during international humanitarian efforts, states with different geopolitical interests may unite to provide aid to a crisis-affected region. This complexity necessitates negotiation and compromise among coalition members, which can reshape their priorities and foster deeper understanding.
The Role of Power Dynamics in Coalition Formation
Power dynamics play a crucial role in the formation and sustainability of coalitions. Actors with significant political, economic, or military strength often dominate the discourse within a coalition, influencing its strategic direction and goals. Such dynamics can lead to power imbalances that affect decision-making processes and outcomes. For instance, more powerful states may leverage their influence to garner support from weaker members, offering diplomatic support or financial incentives to align interests.
Moreover, the creation of coalitions can be a response to shifts in global power structures. Emerging powers may form new coalitions to challenge established norms or practices, as seen in the rise of BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) as a counterbalance to Western hegemony. This emergence highlights how coalitions serve as a platform for reconfiguration in international relations, allowing actors to navigate power dynamics strategically.
Benefits of Coalitions in Achieving Common Goals
One of the primary advantages of coalitions is their capacity to facilitate the achievement of collective goals. By pooling resources, knowledge, and strengths, actors within a coalition can tackle challenges that would be insurmountable individually. This collaborative approach is particularly effective in addressing multifaceted global issues such as climate change, terrorism, and public health emergencies.
For instance, the coalition formed during the Paris Agreement on climate change exemplifies how countries can unite to achieve shared environmental goals despite differing interests and priorities. Here, states agreed to adhere to common standards and targets, demonstrating that collective action through coalitions can lead to meaningful progress on urgent global issues.
Flexibility and Adaptability: A Key Advantage
Another significant benefit of coalitions is their inherent flexibility and adaptability. In a rapidly changing global landscape, the ability to modify strategies and priorities is essential for success. Unlike formal agreements, which may take considerable time to renegotiate or amend, coalitions can pivot quickly, allowing for rapid responses to new challenges.
This flexibility can also facilitate innovative solutions to complex problems. By fostering diverse collaboration among actors with varying perspectives, coalitions can develop creative and effective approaches that may not emerge within more rigid frameworks. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in international relations, where conditions can shift dramatically, necessitating new strategies and alliances.
The Impact of Coalitions on Global Governance
Coalitions have a profound impact on global governance structures, particularly in shaping international norms and policies. The collaborative nature of coalitions allows for the sharing of best practices and experiences, contributing to the development of standards that can drive collective action on global issues.
International organizations often rely on coalitions to mobilize support for initiatives and maintain momentum around critical issues. For example, coalitions formed in response to public health crises, such as the Global Vaccine Alliance (GAVI), demonstrate how collaborative efforts can lead to improved health outcomes around the world. Through these partnerships, resources are combined, and strategies developed that address urgent health challenges effectively.
The Evolution of Coalitions into More Permanent Structures
While many coalitions are temporary, some evolve into more permanent structures as interests align over time. This transformation often results from repeated collaborations among members, fostering greater trust and integration. The European Union (EU) serves as a prime example of how initial coalitions can mature into lasting political and economic unions.
The EU began as a series of coalitions focused on specific economic and security goals. Over time, it has evolved into a comprehensive political entity that addresses a wide range of issues, from trade to environmental policy. This process illustrates how coalitions can serve as a foundation for more stable and integrated political frameworks in international relations.
Challenges Faced by Coalitions in International Settings
Despite the numerous benefits associated with coalitions, several challenges can hinder their effectiveness. One notable issue is the potential for conflicting interests among members, which can lead to tensions and dysfunction within the coalition. When the objectives of members diverge significantly, it can impede decision-making processes and undermine the coalition's overall success.
Additionally, external pressures, such as changing political landscapes or economic crises, can also affect the stability of coalitions. For example, the withdrawal of a key member due to domestic political shifts can disrupt the coalition's operations and strategies. Thus, maintaining cohesion and commitment among diverse actors in a coalition is crucial for achieving desired outcomes.
Conclusion: The Future of Coalitions in Global Politics
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected and interdependent, the importance of coalitions in international relations is likely to grow. Their ability to bring together diverse actors to address common challenges will be crucial to navigate the complexities of global governance in the coming years. The evolution of coalitions into enduring frameworks, as well as the adaptability they offer in response to new realities, positions them as essential tools for collective action.
The future effectiveness of coalitions will hinge on the ability of member states and organizations to align their interests while maintaining the flexibility necessary to respond to changing global landscapes. As such, understanding the dynamics and benefits of coalitions in international relations will be critical for those engaging in diplomacy and global governance efforts. The collaboration fostered through coalitions not only enhances prospects for achieving strategic goals but also contributes to the broader quest for peace, stability, and prosperity worldwide.
Did you find this article helpful? What benefits do coalitions offer in international relations See more here Education.
Leave a Reply



Related posts