
Democracy: Understanding Representative Governance Today
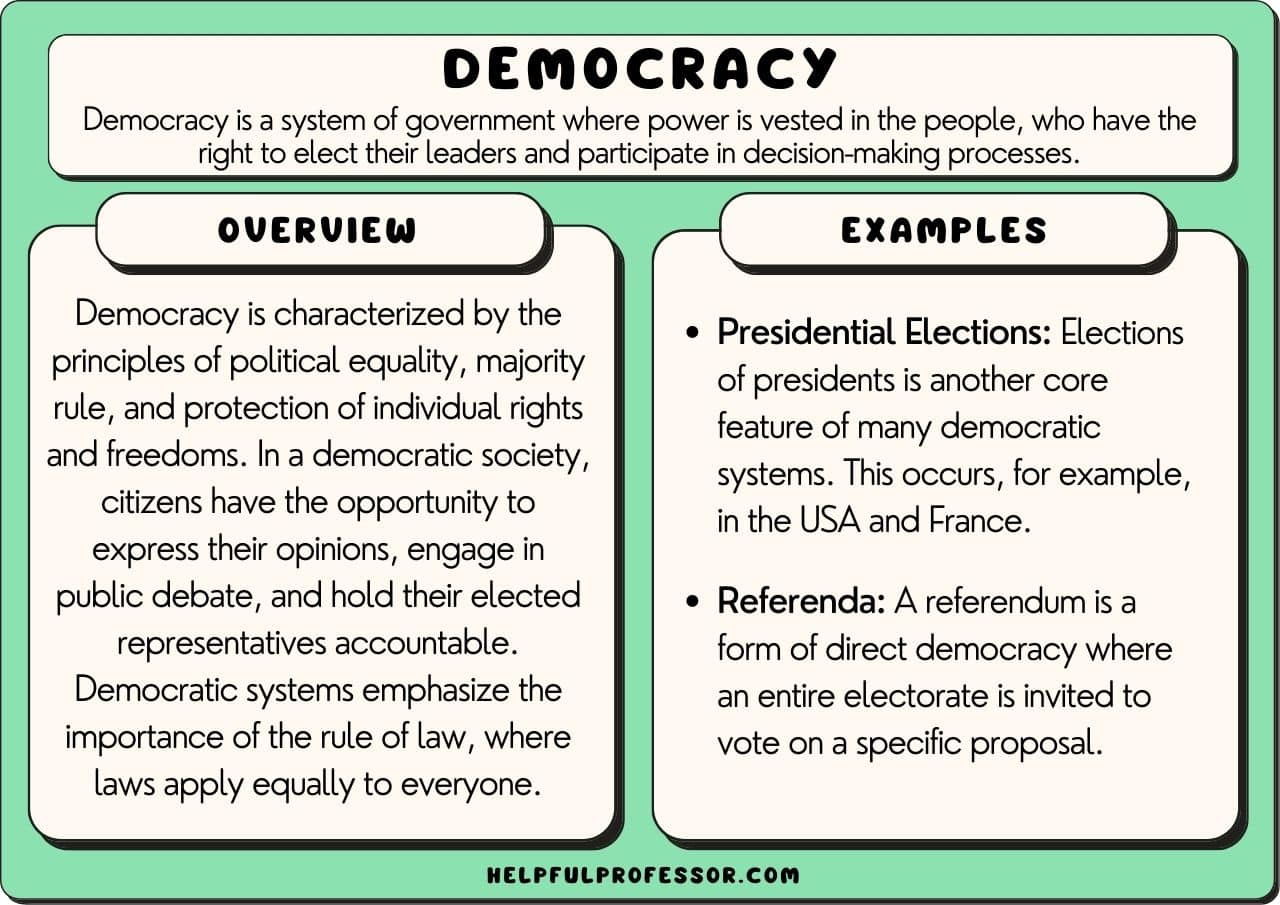
Democracy has always stood as a beacon of hope for societies attempting to strike a balance between governance and the will of the people. The concept of democracy representative governance has undergone significant transformations throughout history, deeply influencing modern political structures worldwide. This article aims to unravel the intricate layers of representative governance, examining its historical foundations and its evolution into the system we recognize today.
From its roots in ancient Greece to contemporary implementations across diverse nations, the journey of democracy representative governance has been anything but linear. Various global events and philosophical movements have played pivotal roles in shaping democratic ideals, leading to the establishment of electoral processes that aim to reflect the voice of the populace. In this exploration, we will delve into crucial historical milestones that have contributed to the development of representative governance, particularly its implications for ensuring individual rights and civic engagement.
- Historical Context of Democracy
- The Evolution of Representative Governance
- The American Revolution and Its Impact on Democratic Ideals
- Constitutional Monarchies: A Compromise Between Tradition and Representation
- Challenges to Representative Democracy Today
- Conclusion: The Future of Representative Governance
Historical Context of Democracy
The inception of democracy representative governance can be traced back to ancient civilizations, primarily in Greece, where the earliest forms of democratic governance were practiced. Cities like Athens marked milestones in political history, establishing a framework where citizens participated directly in legislative decision-making. However, such direct democracy was limited to a select group of male citizens, excluding women, slaves, and foreigners. Thus, while this early model sowed the seeds of political participation, it was far from inclusive.
The Influence of Ancient Greece
The contributions of ancient Greece to the concept of democracy cannot be overstated. The Athenian system of governance introduced citizens to collaborative decision-making, setting a precedent for future democratic practices. In this setting, the principles of representative democracy found their origin, albeit modified over time to allow for broader electoral participation. The use of assemblies and councils showcased how a collective effort could lead to more representative outcomes, a concept that would be embraced and refined in later centuries.
The Evolution of Representative Governance
Evolving from the rudimentary frameworks of governance in ancient Greece, democracy representative began to take shape significantly during the medieval period, especially as the power dynamics within societies changed. By the 1200s, the shift toward including a wider body of citizens—particularly in Europe—was indicative of evolving political structures that began to favor collective representation. Noteworthy movements such as the Magna Carta in 1215 provided a foundational shift towards limiting royal power and advocating for council participation, thereby laying groundwork for parliamentary systems.
The Rise of Individual Rights in the 1600s and 1700s
The Enlightenment era of the 1600s and 1700s heralded a radical transformation in the concept of individual rights, significantly influencing democracy representative. Philosophers such as John Locke, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, and Montesquieu championed ideas of natural rights, social contracts, and separation of powers. These ideas galvanized movements around the globe, particularly among colonists in North America who sought greater involvement in governance against English rule. The emphasis on individual rights laid the foundation for more inclusive notions of government that we now recognize in modern democracies.
The American Revolution and Its Impact on Democratic Ideals
The American Revolution marked a turning point in the global narrative of democracy representative. Following their victory over Great Britain, the United States established a republic characterized by elected representatives, thereby pivoting from monarchical rule to a system where the electorate chose those who governed them. This revolutionary act not only inspired movements in France and Latin America but also set a powerful precedent for civic participation and the belief that governance should reflect the people’s will.
The Emergence of Republics Around the World
In the wake of the American Revolution, the late 18th and 19th centuries saw the proliferation of republican governments globally, fostering a new understanding of political rights and civic engagement. Countries such as France underwent significant political transformations, adopting constitutional principles that gave rise to democracy representative. These republics introduced universal suffrage, albeit gradually, as the world began recognizing the importance of representing diverse populations within political frameworks.
Constitutional Monarchies: A Compromise Between Tradition and Representation
While many nations embraced full republicanism, others opted for constitutional monarchies as a compromise between traditional governance and modern democratic values. This model allowed monarchs to retain a ceremonial role while devolving substantial powers to elected officials representing the people. Examples includethe United Kingdom and Sweden, where the democracy representative structure supports both the monarchy and the parliament, ensuring that the will of the people prevails in decision-making.
The Role of Elections in Modern Democracies
Central to the functioning of democracy representative is the electoral process. Elections serve as the main mechanism through which citizens can express their preferences and influence governance. Various electoral systems—such as first-past-the-post, proportional representation, and ranked choice—have emerged, each with its implications for representation and voter engagement. The integrity and transparency of electoral processes have become paramount, with many nations instituting reforms to enhance voter access and eliminate barriers to participation.
Challenges to Representative Democracy Today
Despite the advancements made in establishing democracy representative, contemporary challenges abound. Issues such as political polarization, disinformation, gerrymandering, and voter suppression pose significant threats to the democratic process. As governments grapple with these challenges, maintaining the integrity and functionality of representative systems becomes crucial to safeguarding the voice of the people in shaping policy and governance.
The Importance of Civic Engagement
To ensure the sustainability and vitality of democracy representative, civic engagement is paramount. Active participation at local, national, and international levels enhances legitimacy and fosters accountability among elected officials. Encouraging dialogue, advocacy, and community involvement strengthens democratic structures by creating an informed citizenry that holds its representatives accountable for their actions. Lifelong learning and civic education become critical components in equipping citizens with the tools necessary to engage meaningfully in the democratic process.
Conclusion: The Future of Representative Governance
As we look to the future of democracy representative, it is imperative to reflect on the lessons from history while being cognizant of contemporary challenges. The evolution of representative governance has led to significant advancements in ensuring individual rights and promoting civic engagement. However, the journey is far from complete. Strengthening democratic institutions, enhancing civic participation, and addressing the challenges of modern governance will determine the trajectory of representative democracies around the globe.
Ultimately, the success of democracy representative depends on the collective commitment of societies to uphold the values of participation, equality, and representation. In fostering environments where every voice matters, we can ensure a brighter future for democratic governance worldwide.
Did you find this article helpful? Democracy: Understanding Representative Governance Today See more here Education.
Leave a Reply



Related posts