
Fruit Bats: Insights into the Fascinating Old World Species
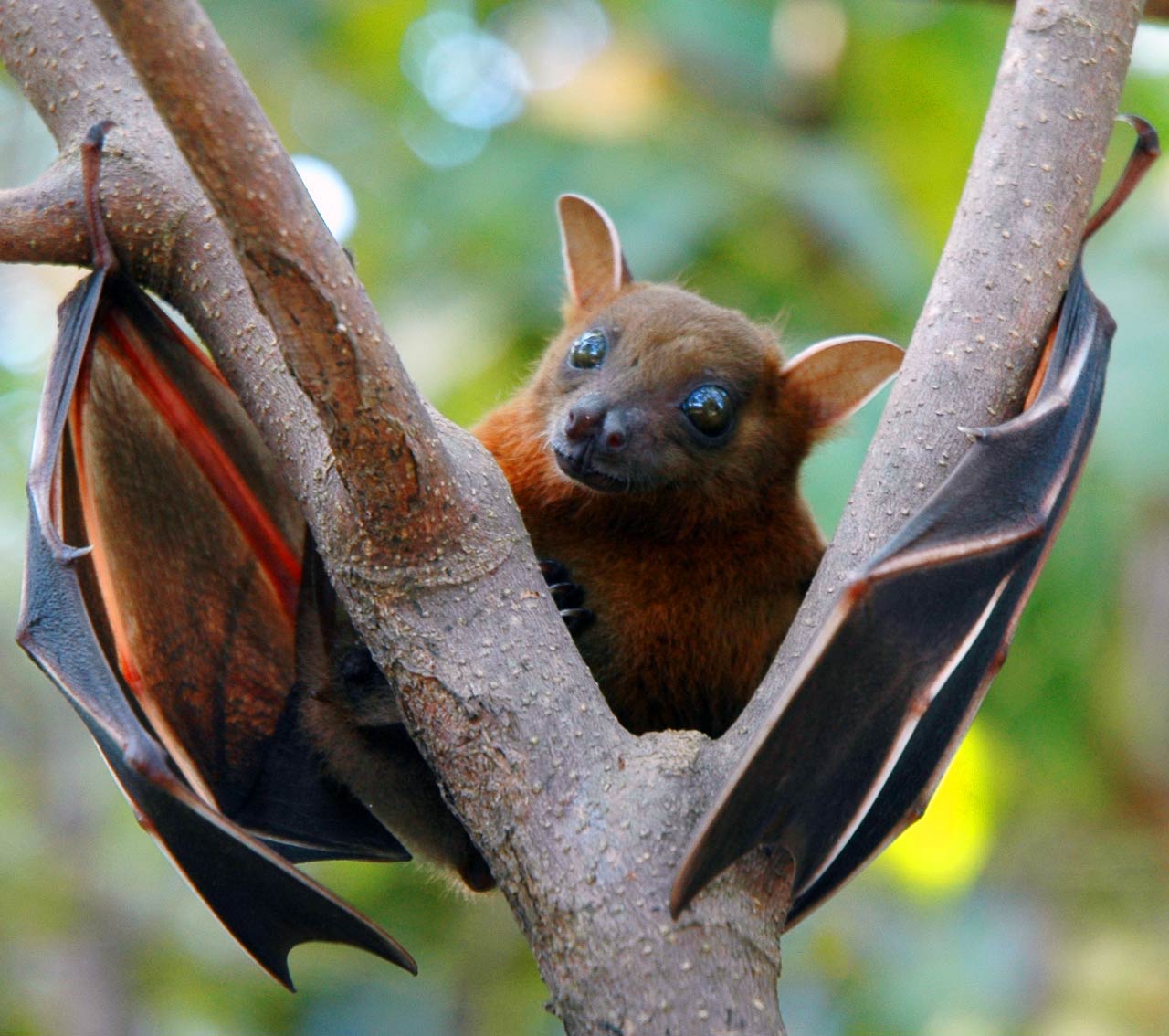

The fascinating world of fruit bats, belonging to the family Pteropodidae, showcases a remarkable diversity of species that not only plays a significant role in their ecosystems but also captures the interest of researchers and wildlife enthusiasts alike. These large-eyed animals, found sprawling across the continents of Africa, Asia, and even Australia, primarily thrive on a diet of fruits and nectar, showcasing their unique adaptations. With over 180 existing species, the Old World fruit bat family provides a glimpse into the complexity and charm of these exceptional creatures.
As avid foragers, fruit bats can be seen flitting between trees, scouring for ripe fruits and flowers. Their active role in pollination and seed dispersal makes them invaluable to various plant species. This article delves into the fascinating aspects of fruit bats, from their expansive diversity to their complex behaviors, highlighting the importance of conserving these unique mammals and their habitats.
Overview of Old World Fruit Bats
The family Pteropodidae is distinct within the broader order of bats due to its unique dietary preferences and physical adaptations. Unlike their insect-eating counterparts, members of this family, known colloquially as fruit bats, have evolved to exploit a diet primarily based on fruits, flowers, and nectar. They are generally larger than most bat species, with some individuals boasting impressive wingspans. For example, the well-known flying fox (Pteropus) can have a wingspan of up to 1.5 meters.
Fruit bats are predominantly found in tropical and subtropical environments, where the availability of fruit and flowers is abundant. These bats do not rely heavily on echolocation; instead, they have highly developed eyesight that allows them to locate food at dusk and dawn, when they are most active. Their social structures vary significantly, with some species living solitarily while others form large, noisy roosting colonies, often in trees or caves.
Diversity of Species
The Pteropodidae family includes a fascinating collection of species that highlight the biodiversity of fruit bats. Some of the most notable groups include flying foxes, long-tongued fruit bats, and various genera that exhibit unique traits and adaptations.
- Pteropus: Known as flying foxes, these are some of the largest fruit bats and can be found across many islands and coastal regions, with distinctive fox-like faces.
- Macroglossus: Long-tongued fruit bats are adapted for extracting nectar from flowers; their elongated tongues can reach deep into blossoms.
- Cynopterus: Also known as short-nosed fruit bats, they have a varied diet that includes fruits and insects.
- Epomophorus: Commonly referred to as epauletted fruit bats, they are characterized by their furry shoulder epaulettes.
- Hypsignathus monstrosus: The hammer-headed fruit bat is notable for its unique, hammer-like face and large size, making it one of the more unusual members of the family.
Habitat and Distribution
Fruit bats inhabit a broad range of environments, primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions where fruit-bearing trees are abundant. Their distribution spans from the forests of Africa to the islands of Southeast Asia and Australia, each species adapted to the specific characteristics of their habitat. For instance, flying foxes tend to favor mangrove forests and coastal areas, while other species might thrive in dense rainforests.
The adaptability of fruit bats to various environments is also reflected in their roosting habits. They often roost in colonies, making use of large trees, caves, and even man-made structures. This social behavior not only aids in thermoregulation but also offers protection against predators.
The social dynamics of fruit bats can vary significantly across different species. Some of these creatures exhibit solitary tendencies, while others form large colonies that can comprise thousands of individuals. These social structures play a critical role in their survival, influencing their foraging behaviors, reproductive strategies, and even their defense mechanisms against predators.
Fruit bats are generally active during the early evening or dawn. During this time, they engage in social interactions, grooming behaviors, and vocalizations that communicate various messages within their colonies. These social interactions also help reinforce bonds between individuals, which is crucial for their overall well-being and survival in dense environments.
Diet and Feeding Habits
The diet of fruit bats primarily consists of a wide variety of fruits, flowers, and nectar. This frugivorous feeding behavior not only sustains them but also establishes their role as critical seed dispersers in their ecosystems. By consuming fruits and subsequently excreting the seeds, they contribute to forest regeneration and plant diversity.
Different species exhibit specific feeding preferences; for example, long-tongued fruit bats are particularly adapted for sipping nectar from tubular flowers, while others may favor more fleshy fruits. Their ability to locate food largely relies on their keen eyesight, which allows them to discern colors and shapes, crucial for identifying ripe fruits in the dim light of dawn and dusk.
Although the majority of bat species rely on echolocation for navigation, fruit bats have developed a different approach. With their strong reliance on vision, these bats use their large eyes to navigate through their surroundings. Their acute eyesight is complemented by a good sense of smell, which is essential for locating ripe fruits and flowers, especially during low-light conditions.
This reliance on visual cues dictates their roosting and foraging behavior, allowing them to efficiently exploit food sources in their habitats. Additionally, their social interactions further enhance navigation, as colony members can communicate and signal the presence of food sources to others.
Notable Species of Old World Fruit Bats
Among the diverse array of fruit bats found within the Pteropodidae family, a few notable species stand out due to their unique characteristics and behaviors. Understanding these species provides insights into the complexity of the family.
- Pteropus vampyrus: Also known as the Malayan flying fox, this species can weigh over 1 kg and has a wingspan of up to 1.5 meters, making it one of the largest bats in the world.
- Macroglossus minimus: As a long-tongued fruit bat, it is known for its remarkable ability to feed on nectar from deep flowers.
- Cynopterus brachyotis: The lesser short-nosed fruit bat is common throughout Southeast Asia and is recognized for its short snout and small size.
- Epomophorus wahlbergi: This species has distinct fur patterns and is widely distributed across sub-Saharan Africa.
- Hypsignathus monstrosus: The hammer-headed fruit bat, with its unique head shape, is found in the rainforests of Central Africa and is notable for its elaborate mating calls.
Conservation Status and Threats
Many species are also subjected to hunting pressures, as they are often regarded as pests in agricultural areas or are hunted for bushmeat. The impacts of climate change, leading to altered weather patterns and decreased fruit availability, further exacerbate the challenges faced by Pteropodidae species. Conservation efforts are vital to ensure the protection of these fruit bats and their habitats, including establishing protected areas and promoting awareness about their ecological significance.
Conclusion
As we unravel the remarkable lives of fruit bats, it becomes evident that these mammals play a crucial role in their ecosystems, particularly in terms of pollination and seed dispersal. Understanding their behaviors, adaptations, and the threats they face is essential for their conservation. The family Pteropodidae encompasses numerous fascinating species, each contributing to the rich tapestry of biodiversity found across the globe. Protecting these unique fruit bats is not only vital for their survival but also for maintaining the health of the ecosystems they inhabit.
Did you find this article helpful? Fruit Bats: Insights into the Fascinating Old World Species See more here Education.
Leave a Reply



Related posts