
Essential Math Formulas to Know for the SAT: Your Ultimate Study Guide

Essential Math Formulas for the SAT: A Comprehensive Overview
The SAT math section tests a variety of mathematical concepts, and having a solid grasp of essential formulas is crucial for success. Familiarity with these formulas not only helps you solve problems more efficiently but also boosts your confidence on test day. Below is a comprehensive overview of the key formulas you should know.
Algebra and Functions
Understanding algebraic expressions and functions is fundamental to SAT math. Here are some critical formulas to remember:
- Linear Equation: y = mx + b (where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept)
- Quadratic Formula: x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
- Factoring Formulas: a² - b² = (a - b)(a + b) and x² + 2xy + y² = (x + y)²
Geometry and Measurement
Geometry questions often appear on the SAT, so knowing the area and volume formulas is essential. Key formulas include:
- Area of a Triangle: A = 1/2 * base * height
- Area of a Circle: A = πr² (where r is the radius)
- Volume of a Cylinder: V = πr²h (where r is the radius and h is the height)
Statistics and Probability
Understanding data interpretation is vital for the SAT. Key formulas to keep in mind include:
- Mean: (Sum of all values) / (Number of values)
- Median: The middle value when data is ordered
- Probability: P(A) = (Number of favorable outcomes) / (Total number of outcomes)
By mastering these essential math formulas, you will be better equipped to tackle the SAT math section with confidence and precision.
Key Algebra Formulas You Must Memorize for SAT Success
Mastering algebra is crucial for achieving a high score on the SAT, and there are specific formulas that every student should have at their fingertips. These formulas not only help solve problems more efficiently but also save valuable time during the exam. Below are some of the essential algebraic formulas that you should memorize to enhance your performance on the SAT.
Basic Algebraic Formulas
- Linear Equation: The standard form is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
- Quadratic Formula: To find the roots of a quadratic equation ax² + bx + c = 0, use x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a.
- Factoring Formulas: The difference of squares can be factored as a² - b² = (a - b)(a + b).
Functions and Graphing
Understanding the properties of functions is essential for the SAT. Be familiar with these key concepts:
- Slope-Intercept Form: The equation y = mx + b helps you quickly identify the slope and y-intercept of a line.
- Point-Slope Form: Use y - y₁ = m(x - x₁) when you know a point on the line and the slope.
Systems of Equations
You may encounter problems that require you to solve systems of equations. Here are two effective methods:
- Substitution Method: Solve one equation for one variable and substitute it into the other equation.
- Elimination Method: Add or subtract equations to eliminate one variable, making it easier to solve for the other.
Memorizing these algebra formulas and understanding their applications can significantly boost your confidence and accuracy during the SAT. With these tools in hand, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle the algebra section of the exam.
Geometry Formulas: What You Need to Know for the SAT
When preparing for the SAT, understanding essential geometry formulas is crucial for achieving a high score. Geometry questions on the SAT often involve shapes, sizes, and the properties of space, which are fundamental concepts in both the math section and the problem-solving tasks. To excel, you should familiarize yourself with key formulas that pertain to various geometric figures.
Essential Geometry Formulas
Here are some of the most important geometry formulas you should know for the SAT:
- Area of a Rectangle: A = length × width
- Area of a Triangle: A = (base × height) / 2
- Area of a Circle: A = πr² (where r is the radius)
- Circumference of a Circle: C = 2πr
- Volume of a Rectangular Prism: V = length × width × height
- Volume of a Cylinder: V = πr²h (where h is the height)
In addition to these formulas, its important to understand the properties of triangles, such as the Pythagorean theorem, which states that in a right triangle, a² + b² = c², where c is the hypotenuse. This theorem is particularly useful for solving problems involving right triangles and can help you find missing lengths when you have two sides.
Understanding Geometry Concepts
Beyond memorizing formulas, grasping the underlying concepts of geometry will enhance your problem-solving skills. For example, knowing how to calculate the area of different shapes allows you to tackle composite figures by breaking them down into simpler components. Moreover, familiarity with angles, parallel lines, and transversals will prepare you for questions that involve angle relationships, such as supplementary and complementary angles.
Ultimately, mastering these geometry formulas and concepts will not only boost your confidence but also equip you with the tools necessary to tackle the geometry questions effectively on the SAT. Regular practice with these formulas will help solidify your understanding and improve your performance on test day.
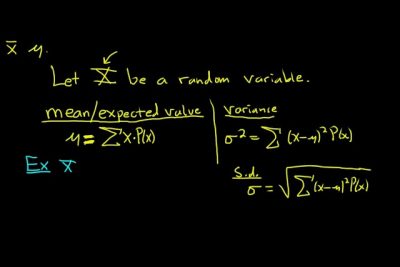
Statistics and Probability: Important Formulas for the SAT Exam
Understanding statistics and probability is crucial for success on the SAT exam. These topics not only appear frequently in the math section but also play a significant role in data interpretation questions. Familiarizing yourself with essential formulas will help you solve problems more efficiently and accurately. Below are some key formulas and concepts you should master.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics provide a summary of data through various measures. Here are some fundamental formulas:
- Mean: The average of a set of numbers, calculated by summing all values and dividing by the count of values.
Formula: Mean = (Σx) / n - Median: The middle value in a data set when arranged in ascending or descending order. If there’s an even number of observations, the median is the average of the two middle numbers.
- Mode: The value that appears most frequently in a data set. A set may have one mode, more than one mode, or no mode at all.
Probability Basics
Probability measures the likelihood of an event occurring. Here are some essential formulas and concepts:
- Probability of an Event: The probability of an event A is calculated as the number of favorable outcomes divided by the total number of possible outcomes.
Formula: P(A) = Number of favorable outcomes / Total number of outcomes - Complement Rule: The probability of an event not occurring can be found using the complement rule.
Formula: P(A) = 1 - P(A) - Independent Events: For two independent events A and B, the probability of both events occurring is the product of their individual probabilities.
Formula: P(A and B) = P(A) × P(B)
Mastering these statistics and probability formulas is essential for tackling the SAT exam effectively. These concepts not only enhance your mathematical skills but also improve your analytical abilities, which are crucial for interpreting data and solving real-world problems.
Tips for Memorizing Math Formulas for the SAT Effectively
Memorizing math formulas for the SAT can seem daunting, but with the right strategies, you can make the process more manageable and even enjoyable. One effective method is to create a formula sheet that includes all the essential formulas you need to know. Organizing them by category—such as algebra, geometry, and statistics—can help you find them quickly when you need to review. Consider using color coding or visual cues to enhance memory retention; for instance, you could use different colors for different math topics.
Another powerful technique is to employ mnemonics. Mnemonics are memory aids that help you recall complex information more easily. For example, you can create a catchy phrase or acronym that relates to a specific formula. This not only makes it easier to remember but also adds an element of fun to your study routine. When you associate a formula with a memorable phrase, you can recall it more quickly during the exam.
Regular practice is also crucial for solidifying your understanding of math formulas. Use flashcards to quiz yourself frequently. Write the formula on one side and its application or a sample problem on the other. This method not only reinforces your memory but also helps you understand how to apply each formula in different scenarios. Additionally, consider forming a study group where you can teach each other formulas and quiz one another. Teaching is a powerful way to reinforce your own understanding.
Finally, don’t forget to incorporate real-world applications of the formulas you are memorizing. When you can connect a formula to a real-life situation, it becomes more meaningful and easier to remember. For example, understanding how the quadratic formula can be used to calculate the trajectory of a ball can help solidify its importance in your mind. By contextualizing the formulas within real-world scenarios, you enhance your comprehension and recall abilities for the SAT.
Did you find this article helpful? Essential Math Formulas to Know for the SAT: Your Ultimate Study Guide See more here General.
Leave a Reply





Related posts