
What is the impact of PAC contributions on elections
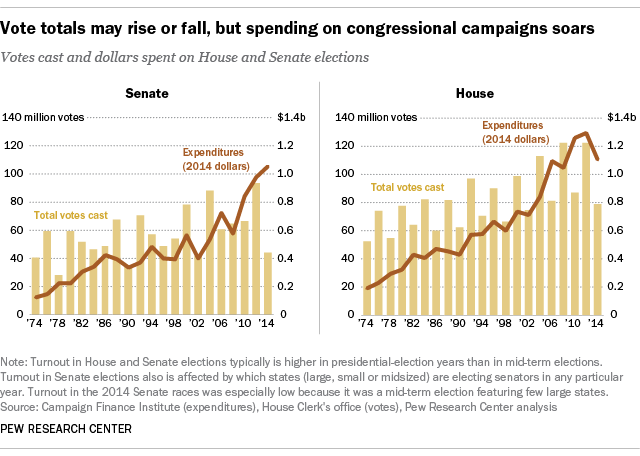
The impact of PAC political contributions on elections has been a growing concern in the landscape of U.S. politics. As organizations that raise and distribute funds to candidates, PACs play a crucial role in shaping election outcomes and influencing policy decisions. Understanding the mechanisms of PAC contributions and their implications for democracy is essential to grasping the contemporary political climate.
This article will delve into the multifaceted world of PACs, exploring their historical evolution, the different types of PACs, their influence on candidate selection, and the broader ramifications of their activities on electoral processes. By dissecting the influence of PAC political contributions, we will highlight how these organizations impact voter behavior, policy formulation, and the overall integrity of the electoral system.
- Overview of Political Action Committees (PACs)
- Historical Context of PACs in U.S. Politics
- The Role of PAC Contributions in Political Campaigns
- Types of PACs and Their Functions
- The Influence of PACs on Candidate Selection
- Legal Framework Governing PAC Contributions
- PACs and Voter Influence: A Double-Edged Sword
- Case Studies: Notable PAC Contributions and Their Outcomes
- The Emergence of Super PACs and Their Impact
- Challenges and Criticism of PAC Influence on Democracy
- Conclusion: The Future of PAC Contributions in Elections
Overview of Political Action Committees (PACs)
Political Action Committees, commonly known as PACs, are vital organizations in the U.S. political framework. They are formed to collect and distribute political contributions to candidates running for various offices, including federal, state, and local levels. PACs can be affiliated with corporations, unions, or interest groups, and their primary function is to support candidates who align with their ideological or policy goals. PACs operate under strict regulations set forth by the Federal Election Commission (FEC), which governs how they collect funds and allocate contributions.
Funds raised by PACs are typically used to finance campaign activities such as advertisements, grassroots organizing, and voter outreach. Understanding the source and impact of these PAC political contributions is crucial, as they can reflect broader social and economic power dynamics in the electoral process.
Historical Context of PACs in U.S. Politics
The history of PACs dates back to the mid-20th century, with the first PAC established in 1944 by the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO). This early organization aimed to support candidates sympathetic to labor issues. However, the true expansion of PACs occurred after the enactment of the Federal Election Campaign Act in 1971. This legislation intended to reduce the influence of large donors and ensure greater transparency in campaign financing. Ironically, it led to an increase in the number of PAC political contributions as organizations began to mobilize smaller donations from numerous supporters.
This change paved the way for the diverse landscape of PACs we see today. In subsequent years, the rise of organizations representing a myriad of interests—ranging from business to environmental causes—illustrated the evolving nature of PAC political contributions in responding to the changing political environment.
The Role of PAC Contributions in Political Campaigns
PAC contributions are a cornerstone of political campaign financing in the U.S. By providing funds directly to candidates, PACs significantly impact the viability of political campaigns. Candidates rely on these contributions to cover the costs associated with running for office, including advertising, staff salaries, and campaign events. The ability of a candidate to attract PAC political contributions often reflects their perceived viability and alignment with particular interest groups.
Moreover, PACs can influence campaign strategies by shaping the narratives and issue frames that candidates adopt. Contributions from a PAC often come with expectations of support for specific policies or agendas once the candidate is in office. This reciprocal relationship raises important questions about who is truly representing the electorate and how much influence special interests hold over elected officials.
Types of PACs and Their Functions
Understanding the various types of PACs is essential to grasping their roles in the electoral process. Broadly, PACs can be categorized into the following types:
- Connected PACs: These PACs are affiliated with a specific organization, such as a corporation or labor union, and primarily collect contributions from members or employees. They support candidates who align with the organization’s interests.
- Nonconnected PACs: These are independent entities established to advocate for specific issues or ideologies without direct affiliation to a corporation or union. They often raise funds from individual donors and focus on a broader range of issues.
- Leadership PACs: These PACs are formed by elected officials or candidates to raise money for themselves or other candidates. They often seek to build influence within their party and support like-minded individuals.
- Super PACs: Emerging after the Citizens United v. FEC decision in 2010, Super PACs can raise unlimited sums of money from corporations, unions, and individuals. However, they are prohibited from directly coordinating with campaigns. Their rise has transformed the landscape of PAC political contributions and campaign financing.
The Influence of PACs on Candidate Selection
PACs exert significant influence over candidate selection in various ways. By endorsing candidates and providing financial support, PACs can help propel lesser-known individuals into the political spotlight. Additionally, candidates often tailor their platforms to align with the interests represented by influential PACs to secure PAC political contributions.
This dynamic can result in a more fragmented representation of interests within Congress, where certain interests are well-funded while others may struggle to gain traction. As a consequence, the ultimate selection of candidates can reflect the balance of power among competing PACs rather than the preferences of the broader electorate.
Legal Framework Governing PAC Contributions
The legal landscape surrounding PAC contributions is complex and has evolved over time. The Federal Election Commission (FEC) regulates PACs, establishing rules on contribution limits, reporting requirements, and the sources of funds. For instance, traditional PACs are limited in the amount they can contribute to candidates, while Super PACs operate under different rules, enabling them to raise unlimited funds from various sources.
These legal frameworks aim to ensure transparency and accountability in campaign financing. However, they also raise critical questions about the effectiveness of regulations in mitigating the influence of money on politics. As PAC political contributions continue to grow, questions about fairness, equity, and the power dynamics at play in elections remain paramount.
PACs and Voter Influence: A Double-Edged Sword
The relationship between PACs and voter influence is multifaceted. On one hand, PACs can enhance voter engagement by mobilizing support around specific issues and candidates. They often educate the public about policy matters, conduct grassroots campaigns, and inform voters about candidates’ positions. This can lead to a more informed electorate that actively participates in the democratic process.
On the other hand, the concentration of PAC political contributions can undermine the democratic principle of equal representation. When certain interests dominate campaign financing, it creates a landscape where the voices of average voters may be drowned out by well-funded special interest groups. This dichotomy highlights the potential harm of unequal influence and raises concerns about the integrity of the electoral process.
Case Studies: Notable PAC Contributions and Their Outcomes
Examining specific case studies reveals the tangible impact of PAC contributions on elections. One notable example is the role of the National Rifle Association (NRA) as a powerful PAC that has effectively mobilized support for candidates who endorse gun rights. Through strategic PAC political contributions and grassroots efforts, the NRA has significantly influenced political races, often leading to shifts in policy direction regarding gun control.
Similarly, environmental advocacy groups, such as the Sierra Club PAC, leverage their contributions to support candidates who prioritize climate action and conservation efforts. Their financial backing enables candidates to compete against well-funded opponents, thus highlighting how PAC contributions can shape candidate viability based on the interests they represent.
The Emergence of Super PACs and Their Impact
The 2010 Supreme Court ruling in Citizens United v. FEC marked a watershed moment for PACs, leading to the rise of Super PACs. Unlike traditional PACs, Super PACs can raise and spend unlimited amounts of money from individuals, corporations, and unions. This new breed of PAC has fundamentally altered the landscape of campaign financing, enabling immense sums of money to flow into elections.
Super PACs remain independent from candidates, yet their expenditures can drive substantial media campaigns and influence public opinion. While they democratize the ability to raise funds for political causes, the concentration of financial power raises alarms about accessibility and equity in the electoral process. As a result, PAC political contributions continue to evoke debate about their ramifications on fair representation.
Challenges and Criticism of PAC Influence on Democracy
The pervasive influence of PACs and their contributions has drawn significant criticism from various quarters. Critics argue that the vast sums of money funneled into elections through PACs undermine the essence of democracy by favoring wealthy donors and organizations who may not represent the average voter’s interests.
Moreover, the reliance on PAC political contributions raises ethical concerns regarding conflicts of interest and the potential for quid pro quo arrangements between politicians and their PAC supporters. These challenges highlight the need for reform in campaign finance laws to ensure that elections remain a contest of ideas rather than a pursuit of financial backing.
Conclusion: The Future of PAC Contributions in Elections
The landscape of PAC political contributions is evolving, influenced by ongoing legal and societal changes. As the political environment continues to shift, the role of PACs in elections will likely also adapt, presenting both opportunities and challenges for candidates and voters alike.
In the coming years, the implications of PAC contributions on elections will remain a pivotal issue, particularly in light of growing concerns about the transparency of campaign financing. Ensuring that the electoral process reflects the diverse opinions and needs of the electorate, rather than the agendas of special interest groups, will be critical for the health of American democracy.
Did you find this article helpful? What is the impact of PAC contributions on elections See more here Education.
Leave a Reply



Related posts