
What are the neck tendons in the human muscle system
The neck is home to a complex system of muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to facilitate a range of movements essential for everyday function. Among these components, the tendons of the neck play a significant role in connecting muscles to bones, enabling the intricate movements of the head and neck. This article aims to explore the anatomy, functions, and importance of these tendons within the human muscular system, as well as the key muscles that interact with them.
Understanding the simple humn anatomy of the neck tendons allows for a deeper appreciation of how interconnected muscle groups contribute to our overall mobility. From rotation and flexion to precise adjustments during daily activities, the coordination of these tendons is integral to maintaining balance and posture, providing the structural support necessary for a healthy range of motion. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of neck tendons and their critical contributions to neck biomechanics.
Anatomy of Neck Tendons
The neck consists of several vital muscles and their associated tendons of the neck, which connect these muscles to the cervical vertebrae and other structures. These tendons can be classified based on the muscles they are associated with and their respective locations in the neck.
Main Tendons and Their Locations
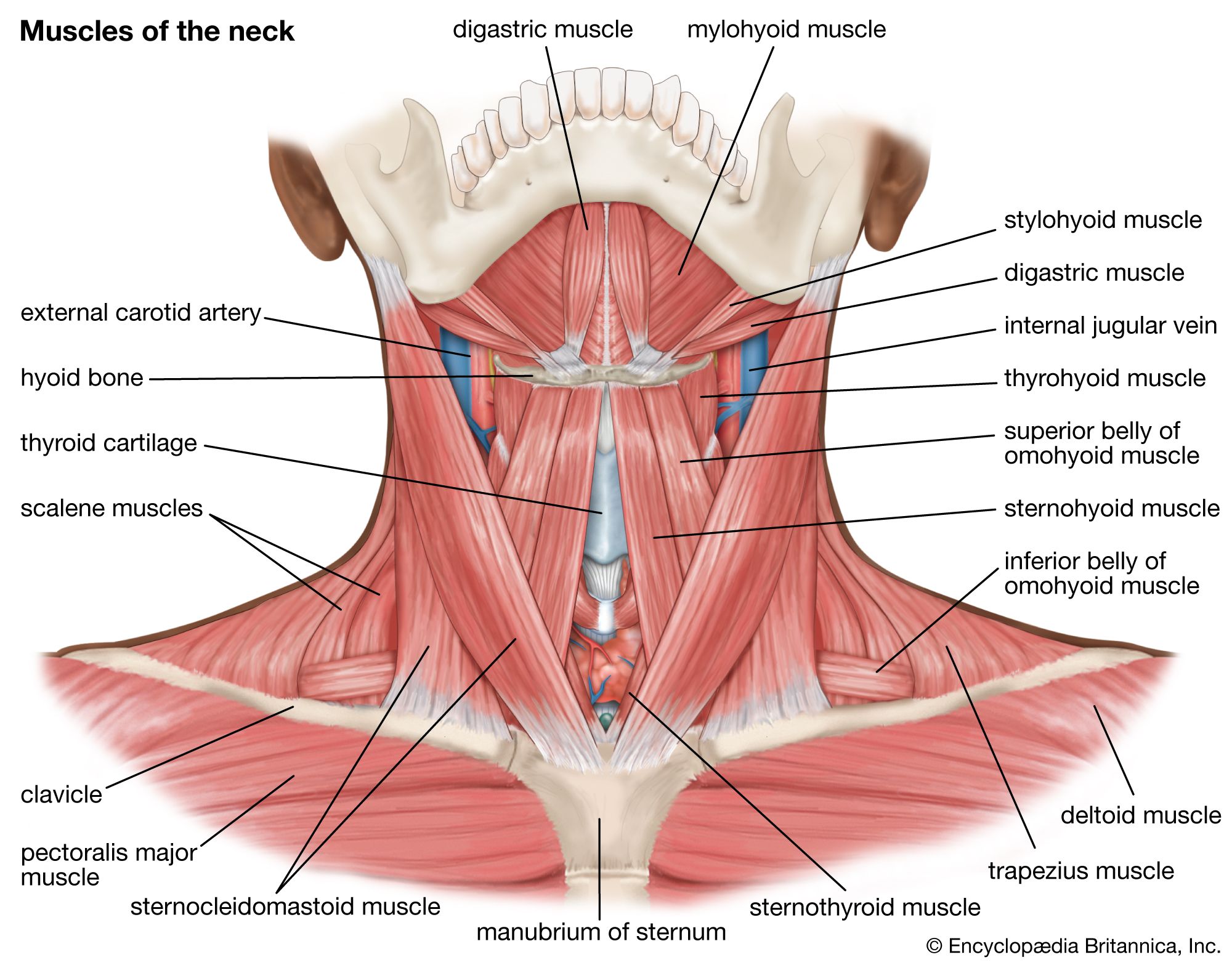
- Sternocleidomastoid Tendon: This important tendon originates from the sternum and clavicle, attaching to the mastoid process of the temporal bone. Its function aids in head rotation and flexion.
- Scalene Tendons: The scalene muscles consist of three bands of muscle that assist in lateral neck movement and respiration. Their tendons attach to the first and second ribs.
- Splenius Muscle Tendons: The splenius muscles help in extending and rotating the head. Their tendons attach to the upper cervical vertebrae and the mastoid process.
- Erector Spinae Tendons: While primarily associated with the back, these tendons also influence neck movement due to their attachment along the spine.
Functions of Neck Tendons in Movement
The tendons of the neck are essential for translating muscle contractions into actual movement. They act as a bridge between the skeletal and muscular systems, providing stability and flexibility. The neck's ability to perform various movements—such as flexion, extension, rotation, and lateral bending—depends heavily on the coordinated actions of these tendons and the muscles they connect.
Movement Mechanics
When a muscle contracts, it pulls on its associated tendon, which in turn pulls on the bone it is attached to. This process allows for locomotion and posture maintenance. For instance, when the sternocleidomastoid muscle contracts, it causes the head to rotate and flex. Similarly, when the scalene muscles contract, they elevate the first and second ribs during inhalation, emphasizing the role of neck tendons in both movement and respiration.
Key Neck Muscles and Their Roles
The neck houses several key muscles, each with specific functions and contributions to movement. These muscles work synergistically, enabling a range of head and neck motions.
The Sternocleidomastoid: A Critical Muscle
Arguably the most recognizable muscle in the neck, the sternocleidomastoid is pivotal for various movements such as rotation, flexion, and lateral bending of the neck. Its unique structure allows it to pull on two distinct points—one on the sternum and one on the clavicle—while attaching to the skull. This geometric arrangement provides powerful leverage, making it a central player in head motion.
Contributions of the Scalene and Splenius Muscles
The scalene muscles consist of three distinct muscles: anterior, middle, and posterior scalene. Collectively, they facilitate lateral and forward flexion of the neck while playing a crucial role in respiration by elevating the first two ribs. The splenius muscles, on the other hand, are responsible for extending and rotating the head and neck, allowing for dynamic positioning during activities such as looking over one's shoulder.
Role of the Erector Spinae in Neck Movements
While primarily associated with spinal extension and posture, the erector spinae also plays a significant role in neck movements. These muscles are positioned along the back and, due to their reach, can assist in extending the neck and controlling its movement during various activities. Their interconnectedness with the muscles of the neck highlights the importance of whole-body coordination during movement.
Importance of Coordination in Neck Movement
Coordination among the neck muscles and their tendons of the neck is crucial for safe and effective head movement. Proper alignment and synchronous contraction reduce the risk of injury and enhance performance during both physical activities and daily tasks. A lack of coordination can lead to strain, tension, and chronic pain due to overactive or underactive muscle groups.
Neuromuscular Control
Efficient neck movement relies on the body's ability to communicate signals between the brain and the muscles through the nervous system. Proper neuromuscular control ensures that the simple humen can execute movements smoothly without compromising stability. This is especially important during dynamic activities such as sports or quick head movements, where unexpected twists or turns can occur.
Conclusion: Understanding Neck Tendons and Muscle Interconnectivity
The tendons of the neck are essential components of the human muscular system, enabling a wide range of movements through the intricate interactions of muscles. Understanding the anatomy and function of these tendons alongside key neck muscles like the sternocleidomastoid, scalene, and splenius reinforces the interconnectivity necessary for efficient movement. Moreover, studying these aspects highlights the importance of maintaining muscle integrity and coordination for overall neck health and functionality. As we appreciate the complexity of the neck's anatomy, we gain insight into our body’s capabilities and the importance of preserving this vital region of our anatomy for optimal quality of life.
Did you find this article helpful? What are the neck tendons in the human muscle system See more here Education.
Leave a Reply






Related posts