
Sodium Oxide: Definition, Common Name, and Uses Explained
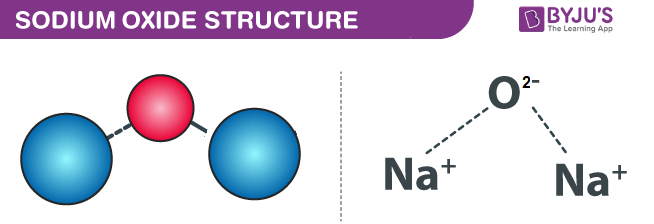
Sodium oxide, with the chemical formula Na2O, is an important compound in the field of chemistry and materials science. In this article, we will explore the definition, common name, and uses of sodium oxide extensively. Understanding sodium oxide is vital for multiple industries, as it plays a significant role in various applications ranging from glass manufacturing to chemical reactions.
Many people may not recognize the name sodium oxide, but its presence and impact are undeniable. This compound serves crucial functions in several industrial processes and is instrumental in producing materials we encounter daily. By diving deeper into sodium oxide, we can uncover its chemical properties, common applications, and safety protocols necessary for its handling.
What is Sodium Oxide?
Sodium oxide is a binary compound made up of sodium and oxygen. It appears as a white solid that can exist in various forms, typically as a powder or a crystalline structure. When sodium oxide comes into contact with water, it reacts vigorously to form sodium hydroxide, a highly caustic substance. This characteristic reaction showcases the highly reactive nature of sodium oxide.
This compound is primarily obtained through the direct combustion of sodium in the presence of oxygen or by the thermal decomposition of sodium carbonate. The formation of sodium oxide can also be observed in various natural phenomena, reinforcing its significance in both industrial and environmental contexts.
Common Name for Sodium Oxide
The common name of sodium oxide is quite straightforward and typically referred to simply as "soda." However, in a scientific or industrial context, it is essential to call it by its correct name – sodium oxide. This compound is different from sodium hydroxide, which is often confused with sodium oxide due to the similarity in their names and the presence of sodium in both chemicals. Understanding the distinction between these names helps in correctly applying their uses and understanding their properties.
Chemical Properties of Sodium Oxide
Sodium oxide is characterized by several significant properties critical to its functions and applications. In its pure form, sodium oxide acts as a strong basic oxide, which means it readily reacts with acids to produce salts and water. Its alkaline nature makes it a valuable nucleophilic agent in many reactions.
Additionally, sodium oxide has a high melting point of approximately 1,132 degrees Celsius (2,070 degrees Fahrenheit). This property makes it suitable for high-temperature applications. It can also absorb moisture from the environment, turning into caustic sodium hydroxide when hydrated, which is a crucial consideration in storage and handling.
Uses of Sodium Oxide in Industry
The applications of sodium oxide in industry are numerous and varied. One of the most significant applications is in the glass-making industry. Sodium oxide is used as a flux, which lowers the melting point of silica, making it easier to melt and work with during glass production. This application is vital for producing various types of glass, including tableware, containers, and construction materials.
- Glass Manufacturing: Sodium oxide is essential in creating different glass types, including borosilicate glass.
- Ceramics: It plays a role in producing ceramics by aiding in the bonding of different materials.
- Chemical Production: Sodium oxide is used in various chemical reactions, acting as a catalyst or reagent.
Applications in Glass and Ceramics
Within the glass and ceramics sectors, sodium oxide serves as a critical component due to its favorable properties. In glass production, sodium oxide helps to create clear, strong glass by facilitating the melting process of silica, thereby reducing energy consumption during production.
Similarly, in ceramics, sodium oxide enhances the durability and stability of finished products. It contributes to the formation of glassy phases within ceramic materials, which improves their strength, thermal shock resistance, and overall performance in various applications such as tiles, pottery, and sanitary ware.
Role in Chemical Reactions
Sodium oxide also plays a significant role in various chemical reactions. It acts as a basic oxide, readily reacting with acids to form salts and water, thus making it an excellent candidate for acid-base chemistry experiments and industrial processes. Moreover, sodium oxide can serve as a precursor in synthesizing sodium compounds, which are vital in numerous applications ranging from agriculture to pharmaceuticals.
In addition, the compound can participate in high-temperature reactions, particularly during the production of ceramics and glass, where it aids in facilitating cross-reactions between different oxides, leading to the formation of complex materials.
Safety and Handling Precautions
To ensure safety during handling, personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats should always be worn. In addition, it is essential to work in well-ventilated areas and utilize appropriate storage containers to minimize the risk of moisture absorption and unwanted reactions.
Conclusion
sodium oxide is a vital component in multiple industries, particularly in glass and ceramics manufacturing. Its ability to act as a flux and engage in chemical reactions makes it an essential material in various applications. Understanding the properties, uses, and safety precautions related to sodium oxide allows for responsible and effective use in industrial settings.
As we explore more about sodium oxide, it becomes evident that while it may be less recognized, it has far-reaching implications across chemical processes and material production. By appreciating its roles and characteristics, we can maximize the benefits it provides while minimizing any potential risks associated with its handling and use.
Did you find this article helpful? Sodium Oxide: Definition, Common Name, and Uses Explained See more here Education.
Leave a Reply






Related posts