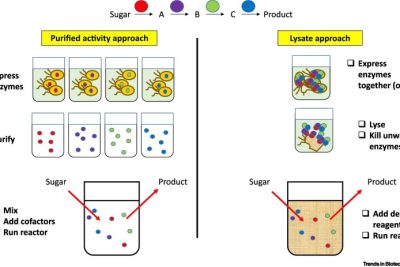
Theories: Exploring Definition, Philosophy, and History

In today's complex world, understanding various theories is essential for navigating the realms of knowledge, philosophy, and science. The study of theories transcends mere classification; it delves into the philosophical underpinnings and historical evolutions that shape our understanding of reality. It’s through this exploration that we can appreciate how different theories have influenced human thought and the advancement of civilization.
From the roots of ancient philosophy to contemporary debates, theories provide frameworks for interpreting existence, knowledge, and social dynamics. This article seeks to provide a comprehensive overview of theories, discussing their definition, philosophical foundations, historical context, and the contributions of key figures throughout history. By examining these elements, we aim to highlight the relevance and lasting influence of theories across various fields.
- Defining Theories: A Comprehensive Overview
- Key Philosophers and Their Contributions
- Aristotelianism: An In-Depth Analysis
- Epistemology: Investigating Knowledge
- Metaphysics: Exploring Existence and Reality
- The Philosophy of Nature: Optimism in the Cosmos
- Aesthetic, Ethical, and Political Dimensions of Theories
- The Enduring Impact of Theoretical Frameworks
- Conclusion: The Continuing Relevance of Theories
Defining Theories: A Comprehensive Overview
The term theories can be interpreted in various contexts, ranging from scientific frameworks to philosophical doctrines. At its core, a theory is an organized set of principles or ideas meant to explain a specific phenomenon or a group of phenomena. In science, a theory is often supported by empirical evidence and is subject to testing and refinement. Philosophically, a theory can refer to a fundamental viewpoint regarding existence, knowledge, morality, or governance.
Understanding the nature of theories involves examining their role in the proliferation of knowledge. Theories serve as lenses through which we can analyze and interpret reality, making them pivotal in both academic and everyday contexts. By establishing analytical frameworks, they allow for systematic exploration, and can lead to new insights and perspectives.
Philosophical Foundations: The Nature of Theories
The philosophical foundations of theories explore the essence of what makes up a theory and its justification. Questions such as "What constitutes a valid theory?" and "How should theories be evaluated?" draw attention to the **epistemological** and **metaphysical** dimensions prevalent within philosophical discourse. Theories are not merely descriptions of reality; they are constructed based on assumptions, methods, and interpretations that are deeply entwined with human cognition.
Philosophers have long wrestled with defining the nature of a theory. For instance, Karl Popper famously proposed the principle of falsifiability as a criterion for distinguishing scientific theories from non-scientific ones. According to Popper, a theory must be testable and refutable to qualify as a scientific endeavor.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Theoretical Thought
The evolution of theories can be traced back to ancient philosophical traditions. From the pre-Socratic philosophers who sought to explain the universe's origins, to Aristotle's systematic characterization of deductive reasoning, the development of theories has been a crucial aspect of humanity's quest for understanding.
Throughout history, theories have evolved, adapting to new discoveries, societal changes, and philosophical debates. The shift from medieval scholasticism to the Enlightenment period sparked new theoretical paradigms and a refined approach to human knowledge. Figures such as René Descartes contributed to the re-evaluation of theories, emphasizing reason as the main source of authority in knowledge claims.
Key Philosophers and Their Contributions
Aristotle: The Foundation of Many Theories
Aristotle is distillation of the collective knowledge of his predecessors and his original contributions laid the groundwork for many theoretical frameworks in Western philosophy. His works introduce key concepts such as the definitional groundwork for subjects and predicates that form the basis of logical reasoning.
Aristotle's systematization of various domains, ranging from ethics to metaphysics, reflects the interconnectedness of theories. He emphasized empirical inquiry and the importance of categorizing knowledge, laying the foundation for future philosophers and scientists.
Modern Theorists: Building Ultimate Realities
As we move forward in history, philosophers like David Hume and Immanuel Kant sparked debates around empiricism and rationalism, respectively. Hume challenged the idea of causality as a fundamentally reliable premise in scientific theories, while Kant sought to reconcile insights from both schools of thought. These dialogues among theories have spurred progress in epistemology, resulting in more robust theoretical formulations.
Aristotelianism: An In-Depth Analysis
Aristotelianism represents a significant branch of philosophical inquiry, emphasizing observational empirical methods while melding them with logical constructs. This theory profoundly influences various disciplines, including natural sciences, ethics, politics, and aesthetics.
The core of Aristotelianism is the distinction between potentiality and actuality, which allows us to grapple with the nuances of existence and transformation. This framework is crucial in understanding not just philosophical inquiries, but also scientific developments that hinge upon observable change.
Methodological Approaches in Theoretical Philosophy
The methodology of theory construction varies across disciplines yet often shares commonalities. The most prevalent method in theoretical philosophy, particularly in Aristotelian thought, is deductive reasoning. This method allows philosophers to derive conclusions from established premises, reinforcing the credibility of theories through logical consistency.
In addition to deduction, the use of induction fosters a broader exploration of knowledge by drawing generalizations from specific observations. Balancing these methodological approaches enhances the richness and applicability of theories across various fields.
Epistemology: Investigating Knowledge
Epistemology serves as the study of knowledge; examining its sources, validation, and extent. Within this field, theories play a central role in shaping our understanding of truth and belief. Philosophers such as Plato and Descartes have been instrumental in proposing different epistemological frameworks that continue to influence contemporary discussions.
The exploration of propositions and justifications leads to critical inquiries about the nature of belief and the criteria for knowledge acquisition. Within epistemology, the distinction between justified true belief and mere opinion remains a topic of ongoing debate.
Metaphysics: Exploring Existence and Reality
Metaphysics delves into the fundamental aspects of existence, reality, and the universe beyond the physical. Theories within this domain question the nature of being and what it means to exist. Philosophers have proposed various metaphysical frameworks, including materialism, dualism, and existentialism, allowing for diverse interpretations of reality.
Notably, discussions around essential versus accidental properties, as highlighted by Aristotelian metaphysics, provide a foundation for examining the attributes that define an entity. This exploration unearths the complexities of existence and challenges our perceptions of reality.
The Philosophy of Nature: Optimism in the Cosmos
The philosophy of nature examines the universe's inherent qualities and relationships, often promoting an optimistic view of existence. Aristotelian theories advocate that nature is purposeful, inherently invoking a sense of order and direction in the cosmos.
This perspective fosters a belief in the interconnection between human beings and the natural world, encouraging a holistic understanding of existence. By integrating scientific inquiry with philosophical principles, we can appreciate nature's dynamics and its implications for our own lives.
Aesthetic, Ethical, and Political Dimensions of Theories
The ramifications of theories extend deeply into aesthetics, ethics, and politics, shaping how we understand beauty, morality, and governance. Philosophers have long debated the roles of art and ethical principles in shaping human experiences.
In the realm of aesthetics, theories surrounding beauty propose various interpretations that influence cultural and artistic expression. The Aristotelian view of poetry as a reflection of life encapsulates the profound relationship between art and reality.
In ethics, theories regarding morality guide societal norms and individual conduct. Aristotelian ethics emphasizes virtue, proposing that the highest good is achieved through living a virtuous life, one that cultivates intellectual engagement and self-sufficiency.
The Enduring Impact of Theoretical Frameworks
The significance of theories persists through time, influencing diverse fields from science to literary criticism. Theoretical frameworks provide insights that guide research, education, and public discourse. Philosophy, as a discipline, enables us to challenge existing theories while contributing to their development and evolution.
The familiar phrase "the tools we use to think about the world" aptly encapsulates the importance of theories. As new discoveries and societal changes emerge, the adjustment and refinement of existing theories ensure continued relevance in understanding our reality.
Conclusion: The Continuing Relevance of Theories
As we navigate the complexities of modern existence, the study and application of theories remain integral to our intellectual pursuits. From their definitional roots through their philosophical foundations and historical significance, theories provide essential frameworks for understanding the world.
Through the expansive investigation of theories—from Aristotelian principles to contemporary theoretical discourse—we appreciate their multifaceted existence. In an age characterized by rapid change, the enduring nature of theories stands as a testament to human intellect and the perpetual quest for knowledge.
Did you find this article helpful? Theories: Exploring Definition, Philosophy, and History See more here Education.
Leave a Reply



Related posts