
What was the impact of US intervention on Panama Canal trade
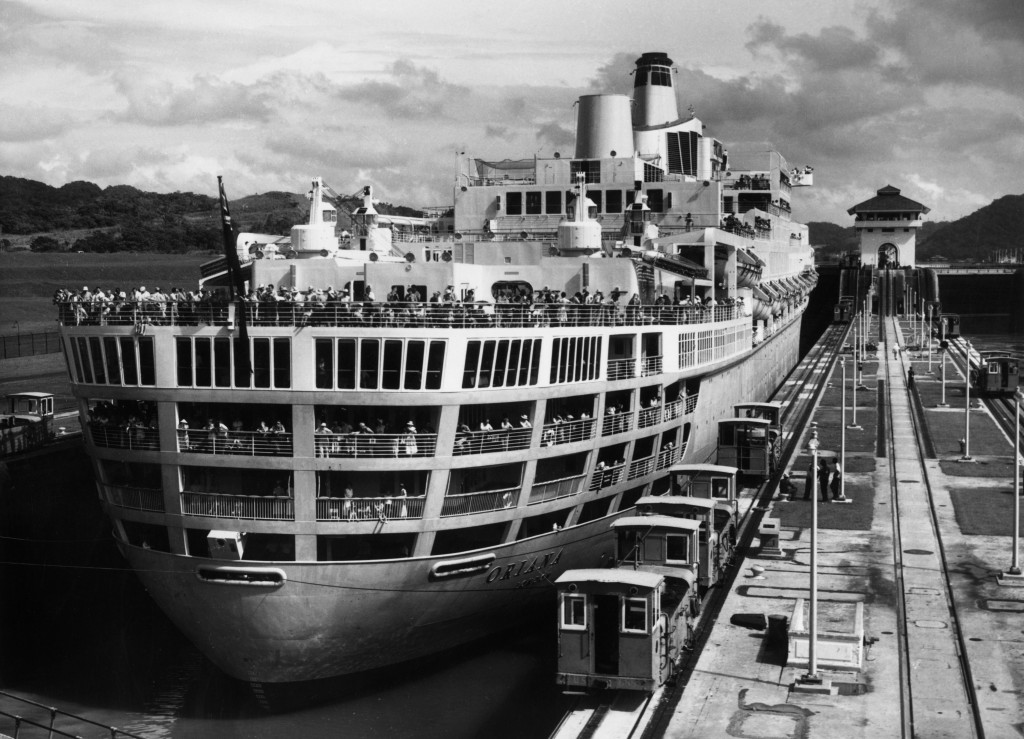

The impact of U.S. intervention on the Panama Canal trade has been significant and far-reaching. As one of the most pivotal engineering feats of the 20th century, the canal not only transformed maritime shipping routes but also reshaped trade dynamics in the Americas and beyond. Understanding this impact requires an exploration of the historical context of the canal’s construction, the challenges it faced, and the socio-economic ramifications of American control.
This article delves into the complexities surrounding the construction and operation of the canal, highlighting the role of U.S. intervention in facilitating trade through this critical waterway. From overcoming tropical diseases to the technology deployed in its construction, the Panama Canal stands as a testament to global connectivity that continues to influence international trade practices today.
- Overview of the Panama Canal and Its Importance
- Historical Context: The Predecessors and Challenges
- The Role of U.S. Intervention in Canal Construction
- Disease Control and the Impact on Labor Force
- The Construction Process: Techniques and Challenges
- The Socioeconomic Impact on Panama
- Trade Developments Post-Opening of the Canal
- The Geopolitical Implications of U.S. Control
- Current Trade Trends Through the Panama Canal
- Conclusion: Long-term Effects of U.S. Intervention on Trade
Overview of the Panama Canal and Its Importance
The Panama Canal is a 50-mile long artificial waterway that connects the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, allowing ships to save thousands of miles of travel. It plays a crucial role in international trade, ensuring more efficient shipping routes and reduced travel time for vessels. As a key transit hub, it has significantly influenced global economic patterns, facilitating trade between the U.S., Asia, and Europe.
Since its completion in 1914, the canal has undergone various operational changes and expansion projects to accommodate larger vessels, known as Post-Panamax ships. This adaptability underscores its continuing relevance in the context of modern trade demands. The ability to transit through the canal not only benefits U.S. tradesmen but also sets the stage for a broader international pay structure related to shipping operations worldwide.
Historical Context: The Predecessors and Challenges
Before the U.S. took charge of construction, the French attempted to build the canal during the 1880s. However, they faced immense challenges, primarily due to tropical diseases like malaria and yellow fever, which devastated the workforce. Many lives were lost during this period, and the attempt ultimately collapsed. The high rate of mortality among the French workers, which reached over 20,000, highlighted the pressing need for a reliable disease control strategy.
The aftermath of the French failure set the stage for American involvement. They not only recognized the need for a feasible canal route but also understood the underlying health challenges that had previously plagued canal construction efforts. The push for American control was driven by strategic military interests and the intention to enhance global trade routes.
The Role of U.S. Intervention in Canal Construction
When the United States committed to building the Panama Canal, it was driven by a vision of facilitating waterborne trade and bolstering its military presence in the region. U.S. intervention began in earnest in 1904 after securing control over the Canal Zone through the Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty. This treaty established a new era in which the United States spearheaded the massive engineering project that had eluded prior efforts.
American engineers and tradesmen, alongside thousands of laborers from the West Indies, took on the monumental task of constructing the canal. With the support of advanced machinery and techniques, they undertook one of the greatest engineering challenges of their time. The intervention not only emphasized America’s engineering prowess but also illustrated its growing influence in the international economy.
Disease Control and the Impact on Labor Force
One of the pivotal factors that distinguished American construction efforts from those of the French was the emphasis on disease control. Under the leadership of Dr. William Gorgas, American medical teams implemented rigorous health measures designed to combat the rampant diseases that plagued the region. This included the widespread use of mosquito eradication tactics, sanitation measures, and worker vaccination programs, which collectively decreased mortality rates significantly.
Despite the advancements, the construction phase was not without its challenges, as 5,609 workers lost their lives from various causes, including accidents and health issues. A workforce of over 40,000 comprised primarily West Indian workers, emphasizing the socio-economic dynamics at play, where labor for U.S. tradesmen came at a cost. Moreover, companies such as J Tech Construction were pivotal partners in the excavation and building processes that shaped the canal.
The Construction Process: Techniques and Challenges
The construction of the Panama Canal necessitated the deployment of innovative engineering techniques in order to overcome the unique geographical challenges the site presented. This included the infamous Culebra Cut, known for its unstable soil and propensity for landslides. In the face of these challenges, American engineers utilized dynamite and steam shovels to excavate around 96 million cubic yards of earth, managing to carve through the mountainous terrain.
- Excavation Techniques: The use of dynamite proved essential in removing vast quantities of earth efficiently.
- Heavy Machinery: Advances in steam-powered equipment enabled more robust construction efforts.
- Safety Measures: Despite improvements, accidents remained frequent due to treacherous working conditions.
As workers continued to face intense conditions, their ability to respond and adapt to the challenges further highlighted the organizational excellence of U.S. construction strategies. The lessons learned during this period laid the groundwork for modern engineering practices and have influenced the standards maintained in construction projects worldwide.
The Socioeconomic Impact on Panama
The construction of the Panama Canal had lasting socioeconomic implications for the local population and the broader region. The influx of American workers and engineers brought economic activity and investment to an area that had previously struggled under colonial rule. However, it also created disparities between the foreign workforce and local Panamanians, who often found themselves marginalized in the economic boom that followed.
The need for skilled labor in the region created a paradox where local tradesmen could not fully participate in the benefits of their labor. Instead, international workers, including those associated with tradesmen international pay, benefitted more from the increased economic activity, leading to tensions between locals and foreign workers.
Trade Developments Post-Opening of the Canal
The Panama Canal officially opened its gates to shipping on August 15, 1914, marking the beginning of a new era in trade development. The canal emerged as a vital conduit for international shipping, drastically reducing travel times between east and west coasts. For example, a journey from New York to San Francisco was shortened by approximately 8,000 miles, allowing businesses to save on time and costs.
Trade patterns shifted significantly as routes became more efficient, encouraging an increase in maritime commerce that globally impacted industries. The canal’s operational model became a standard for other international waterways, showcasing how strategic infrastructure could enhance trade opportunities worldwide.
The Geopolitical Implications of U.S. Control
The U.S. control over the Panama Canal held significant geopolitical ramifications during the early 20th century. It enhanced American influence in Central and South America, allowing the U.S. to project power in a region where it had strategic interests. The canal became a critical military asset, particularly during conflicts such as World War II, when the movement of naval ships was essential.
As both a route for direct military movement and commercial shipping, the canal solidified the United States’ role as a major global power. The international dynamics shaped by the U.S. control of the canal also elicited responses from rival nations, further complicating diplomatic relations in Latin America.
Current Trade Trends Through the Panama Canal
Today, the Panama Canal continues to be a vital artery for global trade. It has witnessed significant expansions and upgrades to accommodate larger vessels and increasing trade demands. The opening of the new locks in 2016 allowed for the passage of Post-Panamax ships, further solidifying its role in the international shipping industry.
Current trends reflect an alignment with growing trade patterns, particularly involving Asia and the Americas. Goods transported through the canal range from agricultural products to electronics, underscoring its continued relevance in international commerce. The strategic location of the canal ensures that it remains a pivotal asset for international trade. Companies worldwide recognize the critical nature of this passage, highlighting the importance of efficient transportation networks.
Conclusion: Long-term Effects of U.S. Intervention on Trade
The long-term effects of U.S. intervention in the construction and operation of the Panama Canal are multifaceted, influencing trade, economic development, and geopolitical relationships. The canal's establishment not only facilitated a dramatic shift in trade dynamics but also highlighted the complexities involved in international construction projects, including labor considerations.
Furthermore, the historical insights gained from the canal's construction reflect broader themes of control, loss, and the enduring impact of American influence in Central America. As current trade trends continue to evolve, it is clear that the legacy of U.S. intervention on Panama Canal trade remains significant, impacting both local economies and global commerce for generations to come.
Did you find this article helpful? What was the impact of US intervention on Panama Canal trade See more here Education.
Leave a Reply



Related posts