
What Is a Sinkhole Definition, Causes, and Impact Explained
Sinkholes are natural phenomena that can occur suddenly and without warning, creating significant hazards to both life and property. Understanding what is a sinkhole is essential for homeowners and city planners, as these occurrences can lead to catastrophic damage. This article aims to define sinkholes, explore their causes, and discuss their impact on the environment and communities.
Sinkholes vary in size and depth, with some appearing as minor depressions while others can engulf entire buildings. The definition of a sinkhole involves not just the physical characteristics of these depressions but also the geological conditions that make them possible. By examining the factors that contribute to sinkholes and their implications, we can better prepare for and mitigate their effects.
What Is a Sinkhole?
Definition of a Sinkhole
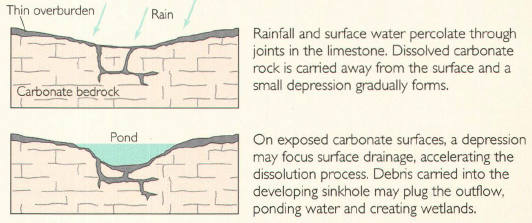
A sinkhole is defined as a depressed area or hole in the ground that results from the collapse of a surface layer into an underground void. This phenomenon is often associated with limestone regions, where the bedrock is easily eroded by water. Sinkholes can vary greatly in size, ranging from a few feet to several hundred feet deep, and can occur suddenly or develop over time.
Common Causes of Sinkholes
Several natural and human-induced factors can lead to the formation of sinkholes. The most common cause of a sinkhole is the erosion of soil and bedrock due to flowing water. Rainwater, which is slightly acidic, can permeate through soil and rock layers, gradually dissolving soluble minerals such as calcium carbonate. This process creates voids under the surface, which can eventually collapse and form a sinkhole.
Geological and Hydrological Factors
The underlying geology of an area plays a crucial role in the development of sinkholes. Regions with limestone, gypsum, or salt deposits are particularly susceptible to sinkhole formation due to the solubility of these materials. Additionally, hydrological factors such as groundwater levels, rainfall patterns, and drainage systems can influence sinkhole occurrences. When heavy rains lead to increased water flow or drainage issues, the risk of sinkhole formation can significantly rise.
Human Activities That Contribute to Sinkholes
In addition to natural processes, human activities can exacerbate or directly cause sinkholes. Construction activities, over-extraction of groundwater, and poor land management practices can disrupt the natural balance of groundwater systems. For example, excessive water pumping can lower the water table, leading to soil compaction and sinkhole development. Urbanization, which often involves the excavation of land and alteration of natural drainage patterns, can also heighten sinkhole risks.
Types of Sinkholes
Different Types of Sinkholes Explained
Sinkholes are generally classified into three main types: solution sinkholes, cover-collapse sinkholes, and contact or subsidence sinkholes. Solution sinkholes form over time as water erodes the rock layer. Cover-collapse sinkholes occur when the material above a void becomes too heavy or saturated, collapsing into the cavity below. Contact or subsidence sinkholes develop when the sediment above a cavern settles or sinks, causing the surface to depress without a sudden collapse.
The Impact of Sinkholes on the Environment
Environmental Consequences of Sinkholes
The emergence of sinkholes can have significant environmental impacts. They often disrupt local ecosystems, causing soil erosion and altering the natural flow of water in the area. This disruption can lead to the destruction of habitats and biodiversity loss, as well as changes in groundwater chemistry and availability. Moreover, sinkholes can compromise the integrity of nearby waterways, affecting water quality and availability for local flora and fauna.
Economic and Infrastructure Consequences
Economic Costs Associated with Sinkholes
Sinkholes can also lead to substantial economic consequences for communities. The costs of repairing damaged infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, can be astronomical. Insurance claims due to sinkhole damage can overwhelm local insurers, leading to increased premiums for homeowners. Furthermore, the economic activity in areas affected by sinkholes may decline due to safety concerns, disrupting local businesses and tourism.
Safety Concerns Associated with Sinkholes
Public Safety and Sinkhole Hazards
Public safety is a critical concern when it comes to sinkholes. These formations can occur with little to no warning, posing risks to pedestrians, vehicles, and nearby structures. The sudden appearance of a sinkhole can lead to accidents, injuries, and fatalities. Proper monitoring and early detection systems can help mitigate these risks, drawing attention to potentially vulnerable areas.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Strategies to Prevent Sinkholes
Preventing sinkholes requires a multifaceted approach that includes proper land use planning, monitoring groundwater levels, and implementing effective drainage systems. Awareness and education about the factors contributing to sinkhole formation are essential for residents in affected areas. Local authorities can take proactive measures such as conducting geological surveys and creating regulations that limit activities that could weaken the ground.
Conclusion: Understanding Sinkholes and Their Implications
In conclusion, understanding what is a sinkhole is vital for individuals and communities living in areas prone to these geological phenomena. By recognizing the definition, common causes, types, and environmental and economic impacts of sinkholes, we can better prepare ourselves and take necessary precautions. The implications of sinkholes reach far beyond mere ground depressions, affecting safety, infrastructure, and local ecosystems. Awareness and proactive management can help mitigate the risks associated with sinkholes, ultimately leading to safer communities.
Did you find this article helpful? What Is a Sinkhole Definition, Causes, and Impact Explained See more here Education.
Leave a Reply






Related posts